Compact Dry SL (Salmonella)
Microval
Characteristics
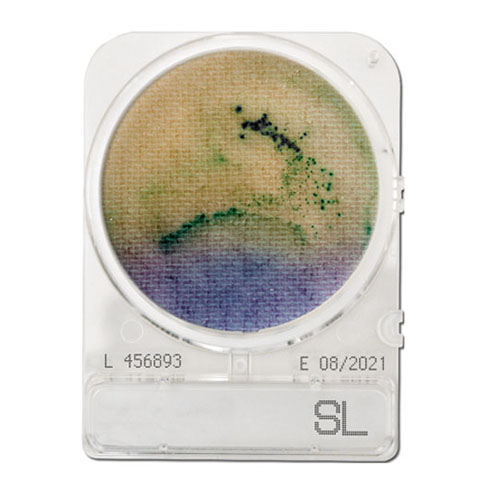
- The presence of Salmonella in the sample is detected by the combination of 3 different test principles, alkalization of the medium (medium color change to yellow), greening colonies (black also), and motility of Salmonella.
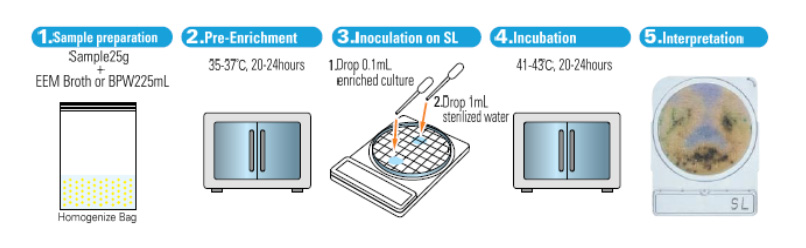
Incubation
- Pre-enrichment culture : 36±1℃ for 20-24 hours
- Incubate at 42±1℃ for 22±2 hours
Result Interpretation
- Salmonella Positive
1. Black to green isolated or fused colonies
2. Medium around the colonies changes to yellow
3. Tailing due to motility - Salmonella Negative
1. No change in plate color
2. Red or reddish-purple colonies
Compact Dry SL is a simple dry culture medium that detects existence of Salmonella qualitatively based on its specific character, such as biochemical reactivity and motility.
Procedures