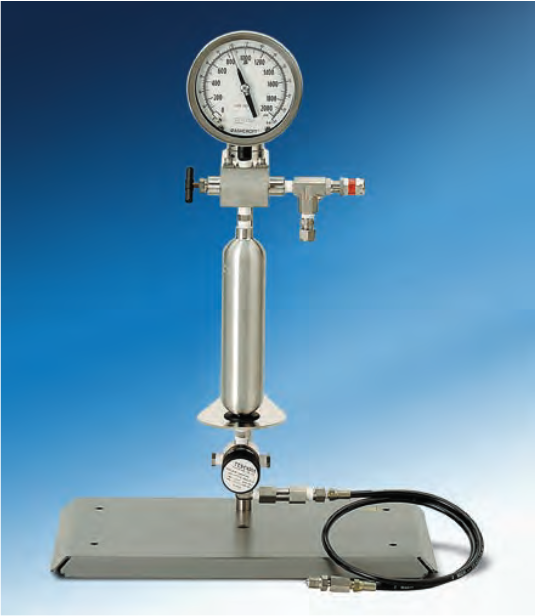
High Pressure Gas Burettes
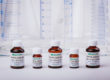
Parr offers a series of high pressure burettes intended to introduce gas (commonly hydrogen) to a reactor at a constant pressure. The burettes consist of a high pressure reservoir equipped with an inlet valve, a pressure gage and a relief valve. A constant pressure regulator with a check valve, a connecting hose and a support stand are included with each pipette.
The amount of gas consumed in a reaction can be determined by knowing the volume of the high pressure reservoir and observing the pressure drop in the reservoir during a reaction
Parr high pressure burettes can be furnished in various sizes as shown in the adjoining , each with a regulator to deliver gas to the reactor over the designated pressure range. The moles of gas shown in the table represent the amount of hydrogen that will be held in the burette at the maximum pressure. The deliverable volume will be a function of the difference in pressure between the pipette and the reactor. The size of the burette selected should be large enough to provide sufficient gas to complete the reaction while still maintaining sufficient pressure in the burette to force gas into the reactor
Reservoirs with larger volumes are available as are regulators with different delivery ranges. Modifications can be made to these basic systems to add an internal thermocouple to the reservoir and/or a pressure transducer for digital readout and/or recording

Liquid Charging Pipettes
To introduce liquids into reactors or vessels at elevated pressures, the most economical way is to use a pressure pipette as a secondary vessel. These are often used for liquid addition to a batch process. Liquid is forced into the reactor from the pipette by applying gas pressure to the pipette greater than the pressure within the vessel. If the passages in the connecting line are large enough, slurries or catalyst suspensions can also be charged into the reactor in this manner.
They include a nitrogen filling connection for attachment to a nitrogen tank. More elaborate pipette systems can be assembled to special order to include additional fittings, such as a pressure gage for the pipette, a pressure relief valve or a large opening ball valve. Special pipettes can also be furnished for higher pressures to 5000 psi
 |
External Catalyst Addition Devices
An external catalyst addition device in the head of a reactor can serve as a convenient solids charging port at atmospheric pressures. The body of this device is machined with an internal taper to aide in the delivery of the solids into the vessel. It has a convenient screw cap closure. The standard seal material is FKM which will accommodate temperatures to 225 °C. Alternate FFKM seals are available for |
 |
Internal Catalyst Addition Devices
Parr has developed a unique device for adding small amounts of solids (or liquids) from a sealed container held within a reactor. It is of particular interest to users performing kinetic studies of catalytic reactions. This device consists of a small cylindrical chamber with a cap that is sealed to the body with an O-ring. It attaches to the underside of the vessel head with a 1/8″ NPT connection. To discharge the contents of the holder, gas pressure is applied through a valve installed on the top of the head. When the applied pressure is greater than the pressure within the reactor, the cap is forced open and the catalyst or other contents of the holder will be released into the reactor. This device works best in the taller, 450 mL and 600 mL Mini Reactors, and in the 1 liter and larger Parr Reactors. |